Mauritius Budget Crisis: 7 Shocking Facts You Must Know
The Mauritius Budget Crisis is an urgent economic challenge facing the island nation, where government policies and financial decisions have created a precarious fiscal situation. This crisis involves a combination of rising public debt, controversial use of central bank reserves, and questionable asset sales, all of which threaten Mauritius’s economic stability. As the government scrambles to bridge budget gaps, citizens and investors alike watch nervously, wondering what the future holds.

The Deepening Mauritius Budget Crisis: Causes and Consequences
The root causes of the Mauritius Budget Crisis lie in persistent government overspending coupled with insufficient revenue generation. Despite raising petroleum taxes and securing record foreign aid from countries such as China and India, the fiscal deficit continues to widen. This fiscal imbalance forces the government to seek unconventional financial measures, like withdrawing billions from the Bank of Mauritius’s reserves. Economists warn that such steps, if unchecked, could spiral into a full-blown financial emergency, undermining investor confidence and economic growth prospects.
Compounding the issue is the lack of effective long-term planning and transparency in fiscal management. The absence of stringent budgetary controls has exacerbated the crisis, making it harder to restore stability. As the government pursues short-term fixes, it risks deepening structural weaknesses that could impair Mauritius’s economic health for years to come.
Government Spending and Debt Growth
The government’s continuous reliance on borrowing to fund its expenditure has resulted in escalating public debt levels, which currently pose a serious threat to fiscal sustainability. Each year, new debt is added to cover deficits rather than financing growth-enhancing projects. This pattern limits the government’s flexibility to respond to future economic shocks and increases vulnerability to external financial pressures. Ultimately, the rising debt burden amplifies the severity of the Mauritius Budget Crisis, making resolution more complex and urgent.
Moreover, the inefficient allocation of resources and growing recurrent expenditures have overshadowed investment in critical sectors, reducing the economy’s competitiveness. Stakeholders emphasize the urgent need for structural reforms to curb wasteful spending and enhance fiscal discipline to manage the crisis effectively.
Why Selling State-Owned Assets Won’t Solve the Mauritius Budget Crisis
In response to the growing budget deficits, the government has announced plans to sell approximately Rs11 billion worth of state-owned enterprises, including MauBank and the National Insurance Company. While such privatization efforts are intended to generate quick revenue, experts argue that this approach is unlikely to bring meaningful relief. Many of these institutions suffer from low profitability and weak market appeal, reducing their sale value and making buyers hesitant.
This reactive strategy risks sacrificing valuable public assets without addressing the underlying fiscal imbalances. Instead of fixing budgetary problems, it may weaken state control over critical economic sectors and deprive the government of steady revenue streams, potentially worsening the Mauritius Budget Crisis in the medium to long term.
Long-Term Implications of Asset Sales
Privatization, if not carefully planned and executed, could have far-reaching negative consequences. The loss of control over strategic sectors may reduce the government’s ability to guide economic development and social welfare initiatives. Additionally, the one-time cash inflows from sales are unlikely to offset growing debt obligations or fund sustainable growth. Analysts caution that without accompanying reforms, asset sales represent a superficial fix that fails to resolve the fundamental causes of the crisis.
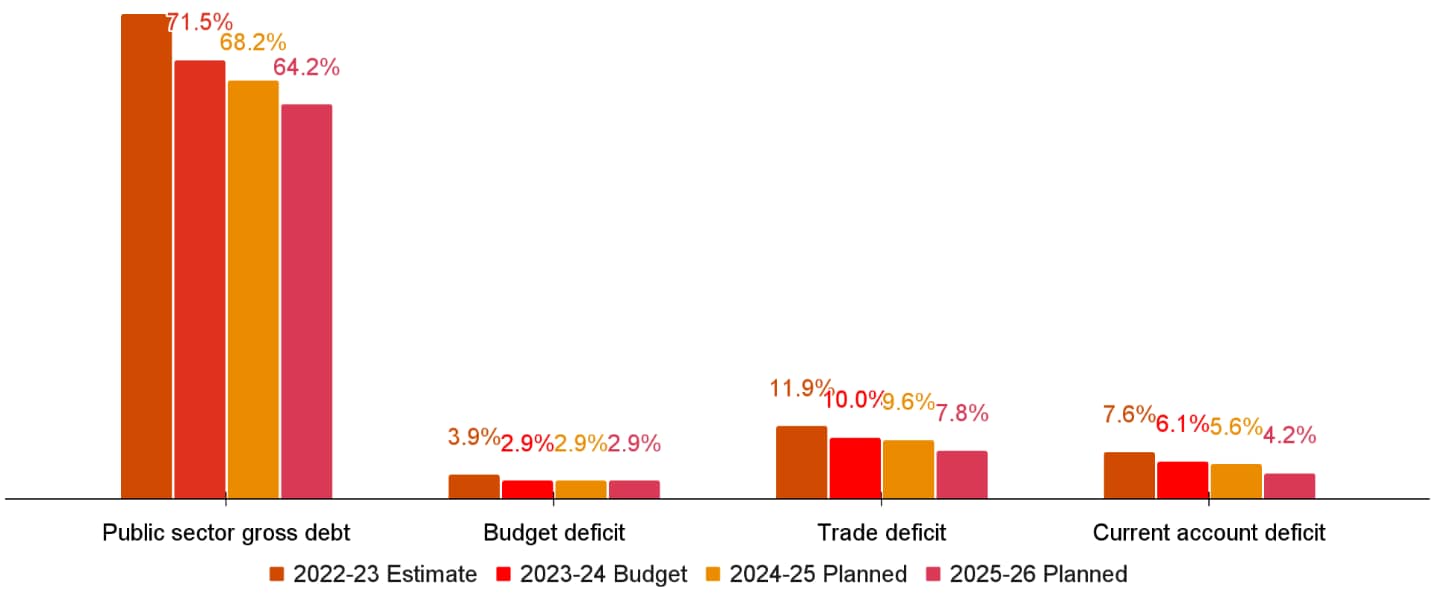
Understanding the Government Debt Strategy Amid the Mauritius Budget Crisis
As part of its debt management strategy, the government is attempting to reduce external debt exposure by shifting towards greater domestic borrowing. This approach is intended to lower foreign exchange risks and reassure international lenders. However, the trade-off involves accepting higher interest costs, as domestic debt usually carries higher rates compared to external loans.
The decision to change the debt mix has implications for both the government’s finances and the broader economy. While it might enhance debt sustainability by reducing currency risk, it may also crowd out private sector credit and increase interest payments, putting additional pressure on public finances. The success of this strategy depends heavily on how well the government balances these competing risks amid the ongoing budget crisis.
The Risks of Increased Domestic Borrowing
Relying on domestic borrowing to finance government operations risks tightening liquidity in the banking sector, which can stifle private investment and economic growth. The Bank of Mauritius has already extended substantial credit to meet urgent fiscal needs, such as the Rs3.5 billion given to the National Property Fund to pay British American Insurance policyholders. Such interventions indicate growing strain on domestic financial resources, complicating efforts to manage the budget crisis sustainably.
Controversy Over Using Bank of Mauritius Reserves in the Budget Crisis
The government’s decision to draw Rs18 billion from the Bank of Mauritius’s internal capital reserves to finance budgetary needs has sparked intense debate. Central banks traditionally maintain reserves to ensure financial system stability and monetary policy credibility, not to fund government deficits. Critics argue that this unprecedented move could undermine confidence in monetary policy and raise legal questions under the Bank of Mauritius Act.
This controversial measure highlights the severity of the Mauritius Budget Crisis and reflects the government’s limited fiscal options. The risk is that tapping central bank reserves may erode the institution’s independence and signal fiscal desperation, potentially deterring investors and triggering adverse economic consequences.
Legal and Monetary Implications
According to the Bank of Mauritius Act, the central bank is restricted from directly financing government deficits. The breach of these provisions could lead to legal challenges and calls for enhanced institutional oversight. From a monetary policy perspective, eroding the central bank’s reserves could limit its ability to control inflation and respond to financial shocks, complicating economic management amid the budget crisis.
How International Perspectives Influence the Mauritius Budget Crisis
The international financial community closely monitors Mauritius’s fiscal situation, with entities like the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Moody’s, and Fitch assessing the country’s creditworthiness. Poor fiscal management and an escalating budget crisis could lead to downgrades, increasing borrowing costs and reducing foreign investment inflows.
Maintaining transparency and fiscal discipline is essential to uphold Mauritius’s reputation as a stable investment destination. International institutions often provide technical assistance and policy recommendations to help countries navigate fiscal challenges, making constructive engagement vital for crisis resolution.
For more detailed analysis, see the IMF Mauritius page, which offers insights into the country’s macroeconomic outlook and policy advice.
Path Forward: Resolving the Mauritius Budget Crisis
Resolving the Mauritius Budget Crisis requires bold and comprehensive reforms focused on improving fiscal discipline, enhancing revenue collection, and optimizing expenditure. Strengthening institutional capacity and adopting transparent budgeting processes will be critical to rebuilding trust and ensuring sustainable public finances.
Additionally, economic diversification and investment in growth sectors can increase government revenues over time, reducing dependence on debt financing. Public dialogue and stakeholder engagement are also essential to foster support for difficult but necessary reforms.
Explore Related Insights on Mauritius Economic Challenges
Readers interested in broader economic trends in Mauritius can visit our detailed analysis on the Mauritius Economic Outlook for up-to-date commentary and expert insights into the country’s financial health and prospects.

Table of Contents
- The Deepening Mauritius Budget Crisis: Causes and Consequences
- Why Selling State-Owned Assets Won’t Solve the Mauritius Budget Crisis
- Understanding the Government Debt Strategy Amid the Mauritius Budget Crisis
- Controversy Over Using Bank of Mauritius Reserves in the Budget Crisis
- How International Perspectives Influence the Mauritius Budget Crisis
- Path Forward: Resolving the Mauritius Budget Crisis
Source: By mauritiustimes